Fill Out a Valid LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation Template
Form Specs
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form is used to determine the electrical load requirements for new construction and renovations in Los Angeles. |
| Compliance | This form ensures compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes. |
| Required Information | Applicants must provide details such as square footage, type of occupancy, and the number of electrical devices. |
| Submission Process | The completed form must be submitted to the Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety (LADBS) as part of the permit application process. |
| Review Timeline | LADBS typically reviews the form within a specified timeframe, which can vary based on the volume of applications. |
| State Law | The form adheres to California's Building Standards Code (Title 24) and the California Electrical Code. |
| Importance of Accuracy | Accurate load calculations are crucial to ensure safety and prevent electrical overloads in buildings. |
| Updates | The form may be updated periodically to reflect changes in codes or regulations, so it is essential to use the latest version. |
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form, it's essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are eight important dos and don'ts:
- Do read the instructions carefully before starting the form.
- Do use clear and legible handwriting or type the information.
- Do double-check all calculations for accuracy.
- Do provide all required information without leaving any blanks.
- Don't use abbreviations that may confuse the reviewer.
- Don't submit the form without reviewing it for errors.
- Don't forget to sign and date the form before submission.
- Don't ignore the deadline for submission; submit it as soon as possible.
Following these guidelines will help ensure your form is processed smoothly and efficiently.
Other PDF Documents
Is It Too Late to Vaccinate My Cat - Store the form in a safe place for future reference.
Wage and Tax Statement - Most employees receive their W-2 electronically or by mail from their employer.
The Illinois Last Will and Testament form is a legal document that allows an individual to outline how they wish their estate to be distributed after their death. This document can specify the allocation of assets among beneficiaries and designate guardians for minor children. Those interested in ensuring their final wishes are respected should fill out the form by visiting https://formsillinois.com.
Geico Supplement - Include a section for additional comments or information as needed.
Common mistakes
-
Missing Information: Many individuals forget to fill out all required fields. This can lead to delays or rejection of the form.
-
Incorrect Load Calculations: Some users miscalculate the electrical load. Double-checking your math is essential to avoid mistakes.
-
Not Following Guidelines: Each section has specific instructions. Ignoring these can result in incomplete or incorrect submissions.
-
Using Outdated Codes: Electrical codes change over time. Ensure that you are using the most current standards when filling out the form.
-
Inconsistent Units: Mixing up units, like watts and kilowatts, can confuse the calculations. Stick to one unit system throughout.
-
Neglecting to Sign: Forgetting to sign the form is a common oversight. A signature is often required to validate your submission.
-
Not Keeping Copies: Failing to make copies of the completed form can be problematic. Always keep a record for your own reference.
-
Ignoring Deadlines: Submitting the form late can lead to penalties. Be aware of all deadlines associated with your application.
Documents used along the form
The LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form is a crucial document for those involved in electrical installations and upgrades. Alongside this form, several other documents are commonly used to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards. Below is a list of these forms and documents, each serving a specific purpose in the electrical permitting process.
- Electrical Permit Application: This document is required to formally request permission to perform electrical work. It includes details about the project, the property, and the licensed electrician responsible for the work.
- Site Plan: A site plan provides a visual representation of the property layout. It shows the location of the building, electrical service points, and any other relevant features that may impact electrical installations.
- Load Calculation Worksheets: These worksheets help in calculating the expected electrical load for a project. They include various factors such as the number of circuits, devices, and the type of occupancy.
- Electrical Plans: Detailed drawings of the electrical system are included in this document. They outline the layout of circuits, outlets, switches, and other components, providing a clear guide for installation.
- Durable Power of Attorney Form: This legal document allows the principal to designate an agent to make decisions on their behalf, even in cases of incapacitation, as detailed at https://californiadocsonline.com/durable-power-of-attorney-form/.
- Inspection Request Form: After the electrical work is completed, this form is submitted to request an inspection by local authorities. It ensures that the work complies with building codes and safety standards.
- Certificate of Compliance: This certificate is issued after an inspection confirms that the electrical work meets all regulatory requirements. It serves as proof that the installation is safe and compliant.
- Manufacturer Specifications: These documents provide important information about the electrical equipment being used. They include details on installation, performance, and safety standards.
- Change Order Form: If any modifications are made to the original electrical plans or scope of work, this form documents those changes. It helps maintain clear communication between all parties involved.
Understanding these additional forms and documents is essential for anyone involved in electrical work. Each one plays a role in ensuring that projects are completed safely and in accordance with local regulations.
Misconceptions
The LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form is essential for ensuring electrical systems meet safety standards. However, several misconceptions can lead to confusion. Here are seven common misunderstandings:
- It’s only for new constructions. Many believe this form is only necessary for new buildings. In reality, it is also required for significant renovations or upgrades to existing electrical systems.
- Only licensed electricians can fill it out. While licensed electricians often handle this, anyone familiar with electrical systems can complete the form, provided they have the necessary information.
- It’s a one-size-fits-all document. Some think the form applies universally to all types of buildings. However, different types of structures may require different calculations based on their specific electrical needs.
- It’s not important for small projects. Many underestimate its importance for smaller projects. Even minor electrical changes can impact load calculations and safety, making the form relevant.
- Filling it out is optional. Some individuals believe submitting this form is optional. In fact, it is often a requirement for obtaining the necessary permits.
- It only considers lighting loads. A common misconception is that the form only accounts for lighting. In truth, it includes all electrical loads, such as appliances and HVAC systems.
- Once submitted, it can’t be changed. Some think the form is final once submitted. However, if changes occur in the project, revisions can be made to the calculations and resubmitted.
Understanding these misconceptions can help ensure compliance with safety regulations and promote effective electrical system management.
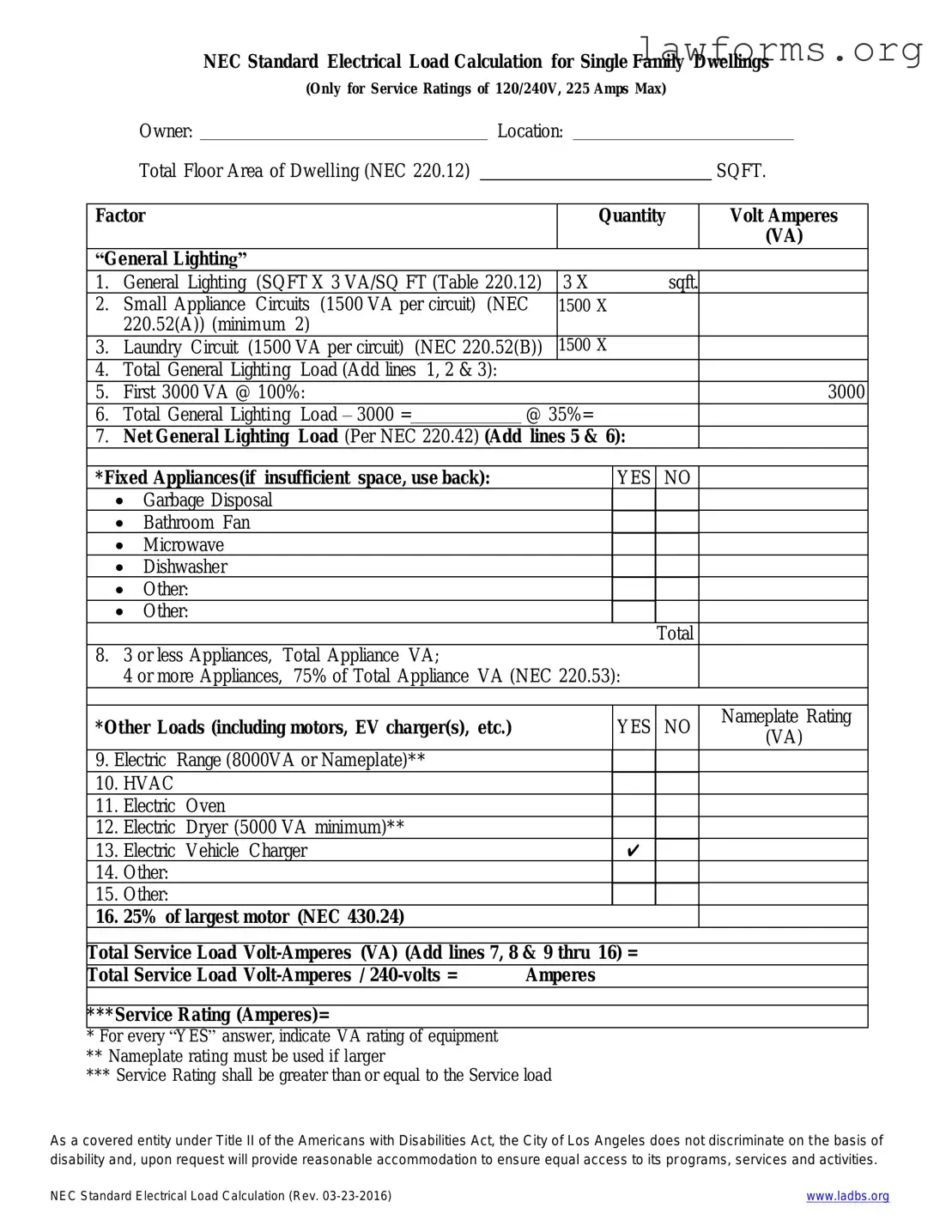
Preview - LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation Form

NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation for Single Family Dwellings
(Only for Service Ratings of 120/240V, 225 Amps Max)
|
|
Owner: |
|
|
|
|
Location: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Total Floor Area of Dwelling (NEC 220.12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SQFT. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Factor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quantity |
|
|
Volt Amperes |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(VA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
“General Lighting” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1. |
General Lighting (SQFT X 3 VA/SQ FT (Table 220.12) |
3 X |
sqft. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
2. |
Small Appliance Circuits (1500 VA per circuit) |
(NEC |
1500 X |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
220.52(A)) (minimum 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
3. |
Laundry Circuit (1500 VA per circuit) (NEC 220.52(B)) |
1500 X |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
4. |
Total General Lighting Load (Add lines 1, 2 & 3): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
5. |
First 3000 VA @ 100%: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3000 |
||||||
6. |
Total General Lighting Load – 3000 = |
|
|
@ 35%= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
7. |
Net General Lighting Load (Per NEC 220.42) (Add lines 5 & 6): |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
*Fixed Appliances(if insufficient space, use back): |
|
|
YES |
NO |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
Garbage Disposal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Bathroom Fan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Microwave |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Dishwasher |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Other: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Other: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
8. |
3 or less Appliances, |
Total Appliance VA; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
4 or more Appliances, |
75% of Total Appliance VA (NEC 220.53): |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*Other Loads (including motors, EV charger(s), etc.) |
|
|
YES |
NO |
|
Nameplate Rating |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
(VA) |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
9. Electric |
Range (8000VA or Nameplate)** |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
10. HVAC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
11. |
Electric |
Oven |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
12. |
Electric |
Dryer (5000 VA minimum)** |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
13. |
Electric |
Vehicle Charger |
|
|
|
|
|
✔ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
14. |
Other: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
Other: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
25% of largest motor (NEC 430.24) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Total Service Load |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Total Service Load |
|
|
Amperes |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
***Service Rating (Amperes)=
*For every “YES” answer, indicate VA rating of equipment
**Nameplate rating must be used if larger
***Service Rating shall be greater than or equal to the Service load
As a covered entity under Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act, the City of Los Angeles does not discriminate on t he basis of disability and, upon request will provide reasonable accommodation to ensure equal access to its programs, services and activities.
NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation (Rev. |
www.ladbs.org |
Key takeaways
When filling out the LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form, keep these key takeaways in mind:
- Accurate Information: Ensure all information provided is accurate and reflects the actual electrical needs of the property.
- Load Types: Identify and categorize all load types, including lighting, receptacles, and appliances, to ensure a comprehensive calculation.
- Calculation Methods: Familiarize yourself with the various calculation methods outlined in the NEC to select the most appropriate for your project.
- Documentation: Attach any necessary documentation, such as equipment specifications or manufacturer data, to support your calculations.
- Review Requirements: Double-check the form for completeness and accuracy before submission to avoid delays in the approval process.
- Consult Regulations: Stay updated on local codes and regulations that may affect your electrical load calculations and ensure compliance.
Following these guidelines will help streamline the process and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Similar forms
The LADBS NEC Standard Electrical Load Calculation form is an essential tool for ensuring that electrical installations comply with safety standards and regulations. Several other documents serve similar purposes in the realm of electrical load calculations and safety compliance. Here’s a list of ten documents that share similarities with the LADBS form:
- National Electrical Code (NEC) - This comprehensive code outlines the minimum safety standards for electrical installations, much like the LADBS form, which helps ensure compliance with these standards.
- Load Calculation Worksheet - Often used by electricians, this worksheet helps to determine the total electrical load for a building, similar to how the LADBS form calculates loads.
- Electrical Service Application - This document is submitted to utility companies to request electrical service and includes load calculations, paralleling the intent of the LADBS form.
- Energy Usage Report - This report analyzes energy consumption patterns and can be used to inform load calculations, akin to the data gathered in the LADBS form.
- Panel Schedule - This outlines the circuits and loads connected to an electrical panel, providing a detailed view similar to the load breakdown in the LADBS form.
- Residential Load Calculation Guide - This guide offers methods for calculating residential electrical loads, sharing the same goal of ensuring adequate service capacity as the LADBS form.
- Commercial Load Calculation Guide - Like the residential version, this guide focuses on commercial settings, helping to determine necessary electrical loads, similar to the LADBS form.
- Energy Audit Report - Conducted to assess energy efficiency, this report often includes load calculations, reflecting the objectives of the LADBS form.
- Electrical Design Criteria Document - This document outlines the design requirements for electrical systems, similar to how the LADBS form sets parameters for load calculations.
- Hold Harmless Agreement: This agreement is pivotal for protecting parties from liability during activities, reinforcing the importance of understanding risks. For a template, you can visit Forms Washington.
- Utility Load Forecast Report - This report predicts future energy demands based on current usage, paralleling the load assessment performed in the LADBS form.
Understanding these documents can empower you to navigate the complexities of electrical load calculations effectively. Each serves a unique purpose while contributing to the overarching goal of safety and compliance in electrical installations.